Introduction
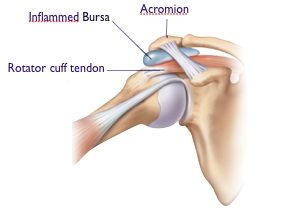
The subacromial space is the area bertween the upper arm bone (humerus) and the acromion (top of the shoulder blade).
This space is filled by a muscle (rotator cuff) and a lubricating sac called a bursa. This fluid sac helps the rotator cuff to glide smoothly beneath the acromion and the AC joint.
The Acromioclavicular joint (AC joint), is the junction where the clavicle (collarbone), attaches to the acromion. The AC joint can undergo degeneration (wear and tear) over time and is usually felt as pain at the end of the collarbone.
In shoulder impingement, the rotator cuff and bursa get pinched between the humeral head and the undersurface of the acromion and the AC joint during overhead activities, resulting in pain.
The operation
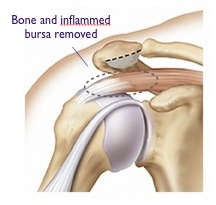
The operation is performed arthroscopically (key hole surgery) through two small puncture wounds.
It involves cutting the ligament and shaving away part of the acromion bone using special instruments. The aim is to increase the size of the subacromial space and decrease the pressure on the rotator cuff.
As the pain may occasionally arise from the AC joint as well,a few mms of the collarbone will be removed arthroscopicaly The aim is to widen the joint and prevent the collarbone from contacting the shoulder blade.
 Loading...
Loading... 


 Arthroscopic
Arthroscopic



